The Porto AFM Workshop 2019 has been announced. This is the sixth edition of the course!
The course will run from the 15th to 18th April. This is a training workshop, aimed at any researcher or scientist, who wants to learn about AFM, or increase their knowledge of the technique. Following the successful courses that have run since 2011, the course will includes several hours hands-on training in acquiring images with the atomic force microscope as well as AFM data processing.
NEWS:
- The course is now full, and no more registrations can be taken. Contact me at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. if you want to me notified about the next course.
- The timetable of the course is here. Note the room change, all lectures are to be given in room 0.36, in the library of the maths department.
Please click the image below to download the flyer with more details.
UPDATES:
- More details of the course will be announced soon, meanwhile, as usual, pre-registration can be made by emailing me at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.. Places on the course are very limited, so interested students should make enquiries or register as soon as possible.
- There will be some guest scientists, talking about advanced applications in different areas. More details will be announced soon
A blog with information and student feedback from the previous courses can be seen here:2017 course, 2014 course, 2013 course, 2011 course.
The course is supported by AFMWorkshop, The Faculty of Sciences of The University of Porto and my research institution, LAQV/Requimte.
- Details
- Hits: 8041
In this article, I’m going to talk about what not to do in AFM. I’ll list 4 mistakes that are common in AFM use, which if you avoid, will certainly improve your results!
-
Using standard settings.This is possibly the worst mistake you can make. AFM imaging is a highly adaptable technique. It’s able to image very large samples of tens of microns with extremely rough topography, or make tiny images of extremely smooth samples with subnanometer features. There is no standard setting which will get good images of all samples. You need to be able to adapt the imaging settings based on the response from the instrument. Optimal AFM imaging is attained through an iterative process! If you don’t know how to optimise imaging of the AFM, I highly recommend revising chapter 4 of my book, “Atomic Force Microscopy”.
-
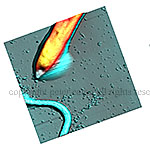
Interpreting image artifacts as image features. It’s important to know which features in your image come from your sample, and which are image artifacts. Learning this can save you some major embarrassment, and a lot of time!
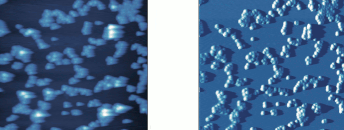 Example of image showing imaging artifacts. being able to spot and correct these artifacts is a crucial skill for an AFM operator. Example of image showing imaging artifacts. being able to spot and correct these artifacts is a crucial skill for an AFM operator. |
- Trying to image dirty or contaminated samples. Sample preparation is the first, and most important part of an AFM experiment. If your sample has a layer of contaminant covering the the part you are interested in imaging, it will make your job almost impossible. Prepare your sample so that it only contains things you want to image.
- “Optimising” your imaging for a nice-looking amplitude (or deflection) image. I was amazed to find people do this. Amplitude and deflection images are made up of the error signal in AFM. The less contrast here is in the error signal, the more accurate your height image is. So, if you optimise imaging to produce a nice-looking high-contrast image in amplitude, you are decreasing the accuracy of your height image!
Avoid these pitfalls and your AFM work should be hassle-free! For help avoiding them I recommend reading my book, “Atomic Force Microscopy”, soon to be released in paperback!
All text and images copyright 2018 Peter Eaton, AFMHelp.com
- Details
- Hits: 10353
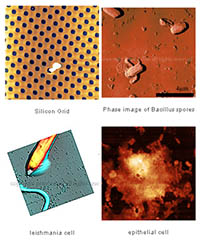 There is a new page here, which is about the recently set up AFM labs in my research institute, Requimte. The page has location, booking information, etc about the labs. But it also has operation protocols for the instruments, so might also be of use for other users of the TTAFM from AFMWorkshop. There are also some example images collected on the two machines, on their individal pages, Long Beach and Signal Hill. The page can be reached directly at afmhelp.com/requimte.
There is a new page here, which is about the recently set up AFM labs in my research institute, Requimte. The page has location, booking information, etc about the labs. But it also has operation protocols for the instruments, so might also be of use for other users of the TTAFM from AFMWorkshop. There are also some example images collected on the two machines, on their individal pages, Long Beach and Signal Hill. The page can be reached directly at afmhelp.com/requimte.
- Details
- Hits: 15427
This instrument is supervised by: Peter Eaton; Please contact Peter for any enquiries regarding access to the lab, or training or use of the instruments. Email: This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
 |
 |
Instrument #1: Long Beach
This instrument is a modified TT-AFM from AFM Workshop.
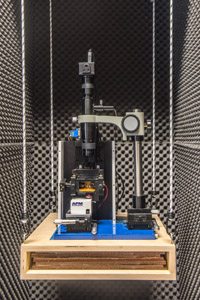
It is equipped with two scanners, enabling large (low resolution) or small (high resolution) sample imaging. It has an standard liquid cell for in-situ measurements, and a custom-made liquid heater cell (ambient to 60 Celsius), with 0.1 degree accuracy. It has been upgraded with two new ADC cards, so it's now capable of recording 12 channels simultaneously, and displaying a life feed of height, scanner voltage, amplitude, etc (see left image above). It's installed in a custom-made vibration and acoustic isolation cabinet.
Here are more detailed specifications:
- Instrument Configuration: Optical lever - based sample-scanning AFM
- Sample Size: Maximum ca. 20x20x5 mm
- Imaging Modes: vibrating (tapping), non-vibrating (contact), phase imaging, lateral force microscopy (friction force microscopy)
- Imaging Environment: Air or Liquid.
- Imaging temperature ambient to 60 ºC
- Z-translation: Vertical direct drive (1 micron resolution)
- XY Translation: Manual
- Video Optical Microscope: Zoom to 400X, 3 micron resolution (3M pixel camera)
- Scan Range: 50x50x17 microns or 20x20x7 microns
- Linearisation: All axes (x, y and z) with strain guages, can be turned off for enhanced signal to noise ratio
- Z noise level: less than 40 picometers
- Vibration isolation: Passive vibration isolation, with acoustic shielding
- Image aquisition: can collect up to 12 channels simultaneously
Instrument #2: San Diego
This is a Life Sciences AFM (model B) from AFM Workshop. It is a probe-scanning AFM with maximum 50 micron scan range. it is mounted on an inverted optical microscope, equipped for brightfield, phase, and fluorescence microscopy. We have both air and liquid scanning-capable probe holders. It is typically used for cell studies and other transparent samples. UPDATE: This instrument currently not available.
Instrument #3: Ontario
Recently installed, this instrument is very similar to the Longbeach instrument, it is a little newer and has the latest (and experimental) software installed.
- Instrument Configuration: Optical lever - based sample-scanning AFM
- Sample Size: Maximum ca. 20x20x5 mm
- Imaging Modes: vibrating (tapping), non-vibrating (contact), phase imaging, lateral force microscopy (friction force microscopy)
- Imaging Environment: Air only.
- Imaging temperature: room temperature
- Z-translation: Vertical direct drive (1 micron resolution)
- XY Translation: Manual
- Video Optical Microscope: Zoom to 400X, 3 micron resolution (3M pixel camera)
- Scan Range: 50x50x17 microns. An optional smaller scanner can be fitted
- Linearisation: All axes (x, y and z) with strain guages, can be turned off for enhanced signal to noise ratio
- Z noise level: less than 50 picometers
- Vibration isolation: Passive vibration isolation, with acoustic shielding
Booking Schedules and Calendars:
Click the link below to see the Longbeach Google calendar
TT-AFM - Longbeach
Or click the link below to see the calendar for "Ontario"
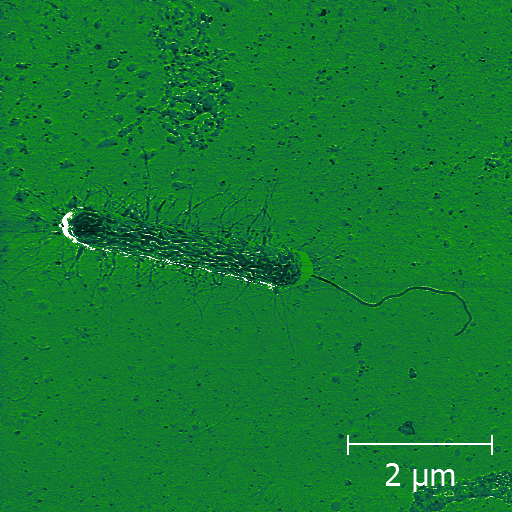
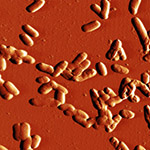
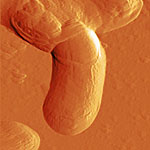
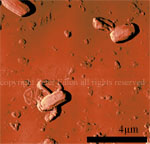
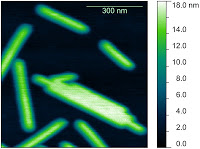
Example Images
Here are just a few example images measured with the TT-AFM (Longbeach) instrument on a variety of samples.
More images can be found in the LS-AFM image gallery and the TT-AFM image gallery.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
TT-AFM Protocols
- Startup Procedure
- Shutdown Procedure
- Insertion and laser alignment of probes
- Scanning in contact "non-vibrating" mode
- Approaching in vibrating mode
- Scanning in tapping or "vibrating" mode
- Opening files: We recommend using Gwyddion version 2.22 or later.
- These protocols may be outdated, meanwhile, here is a link to the latest version of the protocols document for use of "Long Beach": TTAFM_protocols.pdf
Troubleshooting
There is a Google Docs file I have created which contains the solutions to some problems that might crop up using the TT-AFM. This could also apply to other TT-AFM instruments. You can reach it (for viewing) via this link: TT-AFM troubleshooting. If you have something to add to the document, and wish to contribute, just email me (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.) for access.
- Details
- Hits: 29064

 RQUIMTE AFM TWIN LAB
RQUIMTE AFM TWIN LAB
This page has contact information, locations, and other useful information about the AFM instruments in the AFM TwinLabs located in Requimte labs in Porto and Lisbon, Portugal.
This page is intended for users and potential users of the instruments; for more information about Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), see the links on the left. The two labs are equipped with TTAFM instruments from AFM Workshop.
NEWS:
The Porto AFM Workshop 2016 has finished recently, it ran from the from the 18th April to 21st April. This is a training workshop, aimed at any researcher or scientist, who wants to learn about AFM, or increase their knowledge of the technique. Following the successful courses that ran in 2011, 2013 and 2014, the course will included several hours hands-on training in acquiring images with the atomic force microscope as well as AFM data processing. As well as lectures on practical classes, the course featured advanced topics lectures from guest scientists in biology and materials science.
A report on the course was published here recently and the results from the image competition we ran will be announced soon!
A blog with information and student feedback from the previous courses can be seen here: 2014 course, Requimte AFM Workshop 2013
LABS:
| Lisbon lab: Signal Hill | |
 |
 |
| For further details about the facilities in the Porto lab click here or click on the picture above. | For further details about the facilities in the Lisbon lab click here or click on the picture above. |
This site allows users to access instrument specifications and locations, as well as contacts of the two supervisors of the Requimte AFM Twin-lab
· See booking schedule, make bookings at the Twin-lab – for registered users of the instruments only.
· When available you will also see the schedule for Requimte AFM mini-course, and sign-up
· Currently in development: Our protocols for sample preparation, image acquisition, image processing, image analysis. These materials are specifically designed for the individual Requimte instruments. Currently the following procedures are available:
· You can use the following links to download the software required to process the images from the Requimte instruments. This software is Gwyddion, which can be found at Gwyddion.net. There is a user guide for this software here. It is recommended to use version 2.22 or above of Gwyddion. For other AFM/SPM software, look here: SPM Software.
· To access materials specific to one of the labs, click on the lab you are interested in above.
The locations of the two AFM labs in the TWINLAB are shown on a google map linked to below. Click the markers on the map for full address details. Contact details can be found on the pages describing the two instruments linked above (click on the instrument pictures).
Click here to see a google map showing our locations
- Details
- Hits: 44461
Subcategories
Page 5 of 21

