Introduction
This article contains a list of all the software freely available to manipulate data from Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM), that is, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), and Scanning Tunnelling Microscopy (STM). It does not include software designed only to load one particular format, i.e. the software provided by the instrument manufacturers, unless they are able to open other formats. It is intended to summarise the third party software available. It does not compare the quality of the software, and the order is entirely arbitrary. If you know of other software available, let me know. I do know of one other existing list of SPM software[This one], although I dont think it's being updated.
This list is an updated version of that which appeared in my book:"Atomic Force Microscopy", OUP, 2010, with Paul West.
List of Third Party SPM Software
Gwyddion
Freely available, open source software for manipulation of SPM files; supports very many formats, contains many analysis tools. Available for Linux, Windows and MAC OS. Frequently updated. Available here. (http://www.gwyddion.net)
MountainsSPIP
This package loads all of the major formats of SPM files. It is very complete, and produces nice data analysis, including an unusual "report" format of data analysis. Commercial software, but a downloadable demo version is available. Recently merged with SPIP, which was itself extremely popular, into MountainsSPIP 8. DigitalSurf's "Mountains" package also analyses profiler and SEM data.
More details here. (https://www.digitalsurf.com/software-solutions/scanning-probe-microscopy/)
TopoStats
TopoStats is Python package that is designed to batch process AFM images (topography), and extract statisitical information. Can do automated DNA contour tracing. Documentation is here and source code is here.
You need a Python environment to run it.
Software for AFM & SPM data analysis
A community hub for Atomic Force Microscopy and Scanning Probe Microscopy analysis code. Has a few different programs availble, source code only, rather than standalaone packages as far as I can tell. Maintained, or at leat setup, by the AFM and SPM section of the RMS.
WSxM - New - back online!
Freely available software that supports many SPM file formats; and has many analysis tools. I personally like the 3D rendering results from WSxM a lot. It was originally developed by an AFM manufacturer for use with their instrument, but later became completely independent and supports very many other file formats. Unlike many third party programs, has support for force curves as well. Was frequently updated and available here. (http://wsxm.eu) - This new link is a new website, hosting the software.
FemtoScan Online
Commercial software from a manufacturer, but loads lots of (about 20) other formats. 30-days trial has no functional limitations. English and Russian user interface. It seems to be quite capable software, if a little cryptic. Available here. (http://www.nanoscopy.net/en/Femtoscan-D.php)
PyJibe
This is a nice-looking package for manipulaiton of NanoWizard force-distance data including force maps. Free to use, and available here. (https://github.com/AFM-analysis/PyJibe)
PUNIAS (Protein Unfolding and Nanoindenation Analysis Software)
Commercial software, dedicated to analysis of force curves, supports several formats. Implements several of the common analysis techniques used for force spectroscopy, and nanoindentation data. Also supports force volume images. A licence must now be purchased to use it. Available here. (http://punias.free.fr/)
AtomicJ
Freely available, open-source software, with versions for Windows, Mac and Linux. Like PUNIAs, this software concentrates on batch processing of force curves. Opens a small number of common file formats. Seems quite complete, and delivers thoroughly summarised results. Available here, and described in this paper.
Some Matlab scripts to help with nanotribology research - i.e. friction measurements with the AFM. They are for Nanoscope files only. Available here. (http://nanoprobenetwork.org/software-library/welcome-to-the-carpick-labs-software-toolbox) (last time I checked this page had been "temporarily" taken down)
Image SXM
A version of NIH Image that has been extended to handle the loading, display and analysis of scanning microscope images. Seems to be able to open lots of file formats, but only works on MAC, so I've never tried it. Available here. (http://www.liv.ac.uk/~sdb/ImageSXM/)
ImageJ
Cross-platform image analysis program, not specifically designed for SPM images, but there are plugins to load MI or Nanoscope files here. Not very geared towards SPM data, but some people use it, and it does have some useful functions, for e.g. particle counting. Available here. (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/)
GXSM
This is a cross-platform (Linux, with a Windows port) open-source package that not only analyses data, but runs hardware, too. I haven't tried it. More details here.
TrueMap and TrueSurf
True Map is an analysis and display program. TrueSurf is a surface roughness analysis program. These are extensions of profiler software packages, now offering some AFM format support. Commercial software, a licence must be bought for extended use. More details here. (http://www.truegage.com)
OpenFovea
OpenFovea is a program for analysis of force-volume files, i.e. AFM files containing spatially-resolved force curves. It is a Linux-native program with a Windows version also available. I have not tried this software. More details here. (http://www.freesbi.ch/en/openfovea)
Pycroscopy
A package that aims to allow analysis of data from a very wide range of different microscopy methods including AFM / SPM. The program is available as a package for the Python programming language, meaning it's necesssary to install a verison of Python before you can use it. More details here: (https://pycroscopy.github.io/pycroscopy/about.html)
Software that's no longer maintained
SPIP (Scanning Probe Image Processor)
Recently discontinued commercial software for manipulation of SPM files; supports very many formats, contains many analysis tools. Also allows analysis of force curves in several formats. Has a purchase price, but a time-limited demonstration version is available. Frequently updated. Following acquisition of imagemet by digital surf, SPIP has been merged with the MountainsMap package and now it's called MountainsSPIP.
MIDAS 98
Program for deconvolution of AFM files. No longer updated. Appears to only open nanoscope files. Available here.n-Surf
Freeware program to open display and manipulate SPM files. It seems to have most of the common functions, but opens Veeco and NT-MDT only, and appears to be still in beta, and last updated in 2005. The website is available at www.n-surf.com.SPM Image Magic
Note: I welcome comments/suggestions for these lists, please contact me via the "contact" page.
- Details
- Hits: 157658
AFM Manufacturer list
The following is a simple alphabetical list of, hopefully, all the AFM manufacturers in the world. If you have any additions to make, get in touch via the contact form. For AFM probes, look at the SPM Probes list, and for reference samples, see the SPM References list. Note: I have moved the companies that are no longer separate businesses to a new list, below.
- Details
- Hits: 100504
Does an AFM need to be have a technician responsible for it? Or a senior scientist who can train others to use it? In many research labs, the answer seems to be “no”. Or at least, there is no-one fully responsible for the AFM, who can advise on experiment design, sample preparation, and train users, or even just run users’ samples. In this blog post, I’ll talk about why this situation exists, and what should be done about it.
In research labs in academia, (and, to a lesser extent, also in industry), there are often two kinds of facilities, those that are operated by individual researchers, in their own projects, and those that are run either ONLY by technicians /senior scientists, or only by fully qualified researchers under the close supervision of an expert. For example, in chemistry, a common instrument that is usually left to researchers (such as students) to run by themselves, is a UV/visible spectrometer. This is a pretty simple instrument, that is kind of a “black box”, which requires minimal training to use correctly.This is not to say that some things cannot go wrong, but an occasional prod in the right direction is all that’s required. Typically, if any-one is responsible for the instrument, they often just change the bulb now and again. More complex instruments are often run the same way, up to optical microscopes. But this is not the same for nanometre-resolution microscope, right?
Electron microscopes are *rarely* solely user-operated. They nearly always have a technician responsible, who might be the only one to use the microscope at all. When I began to use electron microscopes, it was clear that I was not going to get my hands on the instrument, until after a very thorough training lasting several weeks, and costing a lot of money. After this, I used the instrument for a long period of supervised operation, before finally being considered independent. This makes sense, for several reasons:
-
Electron microscopes are complex, with many controls you need to learn
-
They are easy to misalign, or even damage
-
They usually need careful sample preparation
-
The data from them can need careful interpretation
-
Electron microscopes are (usually) big and expensive instruments
So, what about the AFM? Doesn’t all this hold true for an AFM?
Surprisingly, there are many many cases where AFM instruments do not have a responsible user, let alone a technician. In the AFM training course I teach, something like 50% of the people who need training say there’s an AFM in the lab and no-one knows how to use it.
There are many AFM instruments sitting in lab corners, barely if ever used, or used only by un-trained students.
So, why is this? All those bullets points up there kinda hold true for AFM, don’t they? I think they mostly do, but I think the difference is in the last part.
An AFM can be a low-cost instrument! And an AFM might be very small indeed...which will often lead to the erroneous idea that it’s a simple instrument to use. Is AFM more difficult than electron microscopy? I don’t think so, but most electron microscopists seem to think so. Then again, perhaps this is because they’ve never been trained properly in use of an AFM.
Let’s look at cost; here’s a rough idea of what it costs to get an instrument with 1 nm resolution:
|
TEM |
SEM |
AFM |
|
around 1,000,000 USD |
around 400,000 USD |
40,000 to 100,000 USD |
NOTE: These are “typical purchase costs”, and any of them might costs more or less than this, but not by an order of magnitude….
Now, these 3 instruments would not be the same, and I am not saying a 40,000 dollar AFM can do everything a million dollar electron microscope can do, but with these three instruments, you can achieve around 1 nm resolution. To explain what you can really do with them could make another looong blog post...
But, wow, it’s a big difference, isn’t it? Add to this the fact that a TEM takes up an entire room to itself, and may even need the ceilings raised to fit in (and it usually won’t fit through your door, either!), and you can start to see why sometimes people take the TEM or SEM more “seriously”...If you have to raise a million dollars in funding to buy a microscope, you are going to make damn well sure that a: It’s not broken by incompetent users, and b), that you get some money back to keep it going by selling services.
So there we have our poor little AFM, it’s the new kid on the block, electron microscopists don’t understand it, and no-one ever gets properly trained. Some AFMs are actually installed by technicians who don’t know how to used it.
So what can you do?
-
TRAIN your USERS!
-
MAINTAIN the KNOWLEDGE!
-
keep GOOD staff!
All of these are difficult, but check out our training courses here: http://afmhelp.com/course
I would be interested to hear what other people think about this, it’s something I’ve been telling people a long time, and no-one has contradicted me (audibly) yet! Do people out there who can use AFMs and EMs think one is more difficult than the other? Modern electron microscopes are also highly automated, partially due to more mature technology, and partly, I guess, to justify their high costs!
- Details
- Hits: 25635
One of the most important components of an AFM is the probe. AFM probes are made of a chip or substrate, a cantilever, and a tip. Usually, these are manufactured in one piece of silicon (or silicon nitride, Si3N4), by MEMS manufacturing techniques. In this way a wafer (with 400 or more probes) is manufactured at one time, with reasonable reproducibility of probe characteristics across the probes.
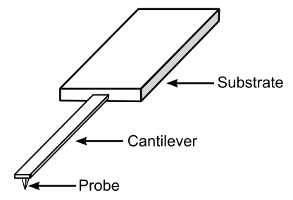
Design of typical AFM probe, showing the substrate, cantilever and tip (probe).
Importantly, nearly all probes are interchangeable, so it’s possible to use probes from different manufacturers in your instrument. Thus, there is a fairly competitive market in AFM probes, and you can find a variety of probes from value to high-cost offerings, and an enormous range of probes, with different coatings, and physical properties, suitable for a wide range of applications. There are so many different probes available that it’s not worth listing them all. This page links to all of the manufacturers of probes (that I know of). Some companies resell probes from other manufacturers, such distributors are listed on this page. But here I list only the manufacturers. The manufacturers are listed in no particular order.
AFM Probe Manufacturers
|
Bruker |
Bruker manufacture a huge range of probes, as well as reselling probes from various other producers. They have many representatives, as well as selling direct in some territories |
|
Applied NanoStructures |
AppNano manufacture a wide range of standard and speciality probes- they are resold by various companies, and also sell direct |
|
Nanoworld |
Nanoworld manufacture a very large range of standard and speciality probes - resold by various companies. Also branded as nanosensors |
|
Mikromasch |
Mikromasch manufacture a very wide range of probes, both standard and speciality. They sell direct and are re-sold |
|
NT-MDT www.ntmdt-tips.com |
NT-MDT manufacture many standard and specialty probes, including with a wide range of coatings |
|
Olympus |
Olympus made many sepcialised AFM probes, notably the biolever, but closed their AFM probe division in 2022 |
|
Artech Carbon |
Artech Carbon make single-crystal diamond probes, which are very sharp and wear-resistant |
|
Team Nanotec |
Team Nanotec make a variety of specialist AFM probes, including metrology tips, high-aspect ratio probes, MFM probes, etc. They both sell direct and are re-sold |
|
Asylum Research |
Asylum make various speciality probes of their own design, as well as reselling various other brands. Asylum are now part of Oxford Instruments |
|
Micro2Nano www.micro2nano.com |
Korean company, Micro2Nano manufacture tetra brand probes which are resold, and offer a custom probe service |
|
Budget Sensors budgetsensors.com |
Budget Sensors manufacture a wide range of probes, including mix-and-match boxes. They have an online shop, and are resold |
|
sQube |
sQube manufacture a range of colloidal probe cantilevers, check their webpage for link to distributor |
|
Kelvin Nanotechnologies www.kelvinnanotechnology.com |
Based on the campus of Glasgow University, Kelvin Nanotechnologies manufacture scanning thermal probes |
|
NaugaNeedles |
Nauganeedles produce specialised probes with semiconductor nanowires grown from the end, useful for metrology and electrical applications |
|
NuNano |
Nunano is a Bristol (UK)-based startup specialising in SPM probe manufacture. Offer custom probe design. |
|
Carbon Design Innovations |
CDI manufacture AFM probes modified with carbon nanotubes on the tip |
|
Smart Tip www.smarttip.nl |
Based in the Netherlands, Smart Tip make specialised probes, such as magnetic MFM probes |
|
Novascan |
Company that specialises in colloid probes and chemically modified probes |
|
SCL-Sensor Tech. |
Company that specialises in self-sensing and self-actuating probes |
|
Rocky Mountain Technology |
Rocky Mountain Nanotechnology specialise in conductive probes, including some specialised probes with solid platinum tips |
Once again, distributors can be found here.
If I any have missed any manufacturers ,or made any other errors, please feel free to make suggestions, via the contact page.
- Details
- Hits: 70099
A very kind mention of our book has been made on the blog from the people at NuNano. This was in an article entitled "12 Brilliant Books on Atomic Force Microscopy". The post is well worth a read, as it covers a lot of the best general texts out there, and some of the more specialised ones as well. Nunano have also been doing quote a lot to create better community around AFM, and their blog is a must-read for me. There is alot of very useful material on their website for the AFM User. Thanks a lot for the kind words, guys!
"This classic text was the starting point from which the website afmhelp.com emerged, run and regularly updated by author Peter Eaton, with the explicit objective to contain all the AFM related material they couldn’t fit into the book! There’s a lot of love for the website from the AFM Community and wholesale agreement that the book behind it is a must-have too."
- Details
- Hits: 12987
Subcategories
Page 1 of 21